Course Home |
Course Policies |
Homework |
Lab Open Hours |
Programming |
Labs |
Schedule & Lecture Notes
Lab Assignment 8
|
Topic:
|
Tree Grafting
|
|
Source Code:
|
graft.cpp
|
|
Live Archive Ref#:
|
3821
|
In-Class Day 1:
|
Tuesday, March 29, 2011
|
|
Submission Deadline:
|
Wednesday, April 6, 11:59pm
|
Techniques:
|
Recursion, Tree traversals
|
Please review the
general information about lab assignments.
Tree Grafting
Trees have many applications in computer science. Perhaps the most commonly
used trees are rooted binary trees, but there are other types of rooted
trees that may be useful as well. One example is ordered trees, in
which the subtrees for any given node are ordered. The number of
children of each node is variable, and there is no limit on the number.
Formally, an ordered tree consists of a finite set of nodes T such that
- there is one node designated as the root, denoted root(T);
- the remaining nodes are partitioned into subsets T1, T2, ..., Tm, each of which is also a tree (subtrees).
Also, define root(T1), ..., root(Tm) to be the children of root(T), with
root(Ti) being the i-th child. The nodes root(T1), ..., root(Tm) are
siblings.
It is often more convenient to represent an ordered
tree as a rooted binary tree, so that each node can be stored in the
same amount of memory. The conversion is performed by the following
steps:
- remove all edges from each node to its children;
- for each node, add an edge to its first child in T (if any) as the left child;
- for each node, add an edge to its next sibling in T (if any) as the right child.
This is illustrated by the following:
0 0
/ | \ /
1 2 3 ===> 1
/ \ \
4 5 2
/ \
4 3
\
5
In most cases, the height of the tree (the number of edges in the longest
root-to-leaf path) increases after the conversion. This is undesirable
because the complexity of many algorithms on trees depends on its
height.
You are asked to write a program that computes the height of the tree before and after the conversion.
| Example input: |
Example output: |
dudduduudu
ddddduuuuu
dddduduuuu
dddduuduuu
#
|
Tree 1: 2 => 4
Tree 2: 5 => 5
Tree 3: 4 => 5
Tree 4: 4 => 4
|
To do for this week
This lab will be our first one split over 2 weeks. In fact, for this part of the lab, I will only ask you to write a function that computes the height of the tree before conversion. Next week, we'll finish off the first version. For now, write a program that does the following:
| Example input: |
Example output: |
dudduduudu
ddddduuuuu
dddduduuuu
dddduuduuu
#
|
Tree 1: 2
Tree 2: 5
Tree 3: 4
Tree 4: 4
|
Hints
Upon first glance, this problem seems like it's going to require you
to build a tree data structure and then implement the conversion from
the general tree to the binary tree. But as is the case with many of
these contest problems, there's a much easier way.
It is possible to compute the resulting depths without ever building
the trees. We suggest a recursive approach. In the end we want a
function that can compute the depth of the entire tree; we will
design a recursion that computes the depth of any subtree. Consider
the following local view:
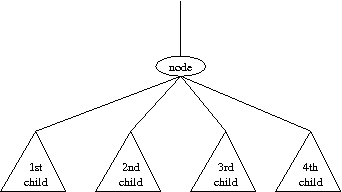
If you were told the traditional depths for each of the four children,
can you compute the traditional depth of the larger subtree?
Consider the "converted" case. If you were told the "converted" depth
for each of the four children, can you determine the converted depth
for the larger subtree?
Here is how we recommend setting up the recursion. Remember that the
original input is just a sequence of 'd' and 'u' designators to
describe the shape of the tree. We want to think about starting the
recursion at the root. Technically, there is no 'd'/'u' pair in the
input for going down to the root up up from it, but for consistency
sake, we recommend that you alter the original input string by adding
a preceding 'd' and a trailing 'u'. Then use a string iterator
to implicitly traverse the tree as you do your computation. Use the
following signature.
int depth(string::iterator& i, bool converted = false);
Assume that the function is called at a time when the iterator is
pointing to the initial 'd' that moves down to a node. This call is
supposed to compute the original (resp. converted) depth of the
subtree at that node, and while doing so it should advance the
iterator so that it is one spot past the final 'u' that designates
moving back up from the given node (note that we pass the iterator as
a non-const reference so that the caller will continue scanning after
the characters that we've processed).
Finally, we've suggested a signature that computes the traditional
depth by default, but can be changed to compute the "converted" depth
by sending a second parameter. Although we could have given two
different functions for the two different depths, we are suggesting a
single function because there is really only a one or two line
difference between the two computations. Still, we recommend that
you start by implementing the traditional depth version. Then you can
go back and do the converted depth. Note that you will make two
separate calls from the main routine, and you will need to
reinitialize the iterator to the beginning of the string for the
second computation.
Pre-lab
Give the output of the lab for the following inputs:
dddduuuduu
dududududu
dudddduuuu
